- Description
- Curriculum
- FAQ
- Notice
- Reviews
- Grade
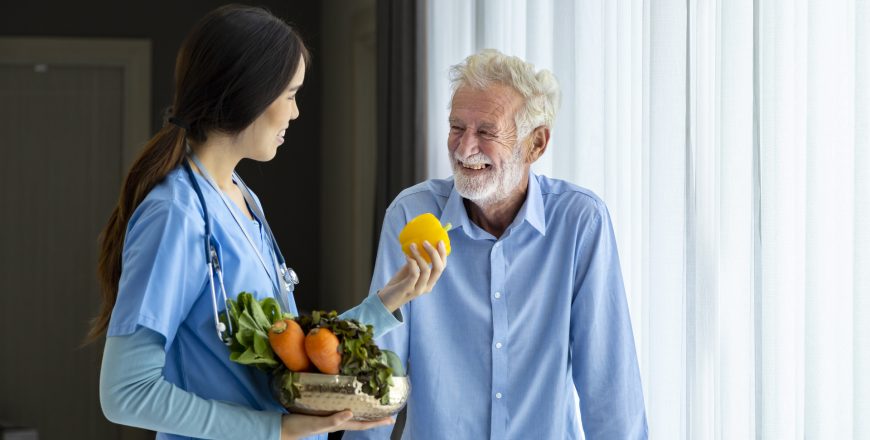
Geriatric health and social care is a multidisciplinary field focused on the well-being of older adults. It encompasses the physical, mental, social, and emotional aspects of aging, recognizing that these factors are deeply interconnected and influence overall quality of life in later years. It’s not just about treating illness; it’s about promoting healthy aging, preventing decline, managing chronic conditions, and supporting older adults to live as independently and meaningfully as possible.
Here’s a breakdown of the key components:
1. Geriatric Health Care (The Medical Component):
-
Focus on Complexity: Older adults often have multiple co-existing chronic conditions (e.g., diabetes, heart disease, arthritis, dementia). Geriatric medicine takes a holistic approach, considering how these conditions interact and impact each other, rather than treating them in isolation. It’s about managing chronic disease, not necessarily curing it.
-
Emphasis on Function and Quality of Life: The goal isn’t just extending lifespan, but also maximizing healthspan (the period of life spent in good health) and maintaining functional independence. This means focusing on things like mobility, cognitive ability, continence, and the ability to perform activities of daily living (ADLs) like bathing, dressing, and eating.
-
Prevention: A strong emphasis is placed on preventive measures, including vaccinations (influenza, pneumococcal, shingles), screenings (for cancer, osteoporosis, cognitive decline), and lifestyle interventions (exercise, nutrition, fall prevention).
-
Medication Management: Older adults are more susceptible to adverse drug reactions due to changes in metabolism and organ function. Geriatric care focuses on “polypharmacy” (the use of multiple medications) and “deprescribing” (safely reducing or stopping medications that are no longer necessary or beneficial). It also looks at drug interactions.
-
Common Geriatric Syndromes: Geriatric care addresses specific conditions common in older adults, often called geriatric syndromes. These include:
-
Frailty: A state of increased vulnerability to stressors, characterized by weakness, fatigue, and decreased physiological reserve.
-
Falls: A major cause of injury and disability in older adults. Prevention and management of fall risk factors are crucial.
-
Incontinence: Both urinary and fecal incontinence, which can significantly impact quality of life and social interaction.
-
Delirium: An acute confusional state, often triggered by illness, medication, or surgery.
-
Dementia: A decline in cognitive function that interferes with daily life. This includes Alzheimer’s disease and other types of dementia.
-
Pressure Ulcers (Bedsores): Skin breakdown due to prolonged pressure, common in those with limited mobility.
-
Malnutrition.
-
Sensory impairments (vision and hearing loss)
-
-
Palliative and End-of-Life Care: A crucial part of geriatric medicine is providing comfort, pain management, and support to individuals with serious, life-limiting illnesses, as well as support for their families. This includes advance care planning (discussing and documenting the person’s wishes for future medical care).
2. Geriatric Social Care (The Social Component):
-
Maintaining Independence and Social Connection: This involves supporting older adults to live in their own homes for as long as possible, if that is their wish. It often involves providing services like:
-
Home Care: Assistance with ADLs, meal preparation, medication reminders, and light housekeeping.
-
Transportation: Helping older adults get to medical appointments, social activities, and errands.
-
Socialization Programs: Adult day care centers, senior centers, and other programs that provide opportunities for social interaction and engagement, combating loneliness and isolation.
-
Respite Care: giving a family member or informal caregiver a break.
-
-
Care Coordination: Navigating the complex healthcare and social service systems can be overwhelming. Care coordinators help connect older adults and their families with the appropriate resources, advocate for their needs, and ensure smooth transitions between different levels of care (e.g., from hospital to home, or from home to assisted living).
-
Housing: Assessing and addressing housing needs, which might include:
-
Home Modifications: Making changes to the home to improve safety and accessibility (e.g., installing grab bars, ramps, stairlifts).
-
Assisted Living Facilities: Providing a supportive living environment with assistance with ADLs and meals, but more independence than a nursing home.
-
Nursing Homes (Long-Term Care Facilities): Providing 24-hour care for individuals with significant medical and functional needs.
-
Continuing Care Retirement Communities– providing a variety of care in one place.
-
-
Financial and Legal Support: Assisting with:
-
Financial Planning: Managing finances, accessing benefits (e.g., Social Security, Medicare, Medicaid), and preventing financial exploitation.
-
Legal Planning: Preparing advance directives (living wills, power of attorney), guardianship, and estate planning.
-
-
Protection from Abuse and Neglect: Elder abuse (physical, emotional, financial, or neglect) is a serious concern. Social care includes identifying and addressing cases of abuse, and providing support and resources to victims.
-
Mental Health Support. Includes therapy, medication management, and support groups for those with depression, anxiety and other concerns.
3. The Interdisciplinary Team:
Geriatric care is rarely delivered by a single professional. It’s typically a team effort involving a range of professionals, including:
-
Geriatricians: Physicians specializing in the care of older adults.
-
Nurses: Including registered nurses (RNs), licensed practical nurses (LPNs), and nurse practitioners (NPs) who specialize in geriatrics.
-
Social Workers: Providing counseling, care coordination, and advocacy.
-
Physical Therapists: Helping improve mobility, strength, and balance.
-
Occupational Therapists: Helping individuals adapt to functional limitations and maintain independence in ADLs.
-
Speech-Language Pathologists: Addressing communication and swallowing difficulties.
-
Dietitians/Nutritionists: Providing nutritional guidance and addressing dietary needs.
-
Pharmacists: Managing medications and preventing adverse drug events.
-
Psychologists/Psychiatrists: Addressing mental health concerns, such as depression, anxiety, and dementia.
-
Caregivers (Family and Paid): Playing a crucial role in providing direct care and support.
-
Audiologists
-
Dentists
-
2Safeguarding And Protection In Care Settings
-
3Q&A Definitions and Principles
-
4Q&A Recognizing Abuse and Neglect
-
5Q&A Reporting Procedures
-
6Q&A Best Practices and Prevention
-
7Q&A Specific Scenarios and Dilemmas
-
8Q&A Personal Reflection and Continuing Development
-
9Q&A Legal Framework and Responsibilities (India)
-
10Test Safeguarding And Protection In Care Settings
-
74Autistic Spectrum
-
75The Lost Generation
-
76Masking and Camouflaging: A Deep Dive
-
77Sensory Sensitivities in ASD: A Deep Dive
-
78Executive Functioning Challenges
-
79Communication Differences
-
80Restricted Interests and Repetitive Behaviors (RRBs)
-
81Co-occurring Conditions in Older Adults with ASD
-
82Social Isolation and Loneliness
-
83Increased Vulnerability to Abuse and Neglect
-
84Recognizing Potential ASD in Older Adults
-
85Assessment Tools and Strategies
-
86Assessment tools
-
87Differential Diagnosis in Older Adults with Suspected ASD
-
88Person-Centered Approach
-
89Key Principles of Care
-
90Environmental Adaptations
-
91Legal and Ethical Considerations
-
92Future Directions
Education: Although there is no minimum requirement, a student have studied upto at least 8th STD
Communication Skills: Excellent verbal and written communication skills, including presentation skills.
Interpersonal Skills: Strong ability to build rapport, establish trust, and maintain relationships.
Analytical Skills: Ability to analyze sales data, identify issues.
Computer Skills: Proficiency in using CRM systems and other computer applications.
Organizational Skills: Effective time management and organizational skills to manage their responsibilities efficiently.
Ethical Conduct: A strong commitment to ethical behavior and compliance with regulations.
Productivity Hacks to Get More Done in 2018
— 28 February 2017
- Facebook News Feed Eradicator (free chrome extension) Stay focused by removing your Facebook newsfeed and replacing it with an inspirational quote. Disable the tool anytime you want to see what friends are up to!
- Hide My Inbox (free chrome extension for Gmail) Stay focused by hiding your inbox. Click "show your inbox" at a scheduled time and batch processs everything one go.
- Habitica (free mobile + web app) Gamify your to do list. Treat your life like a game and earn gold goins for getting stuff done!